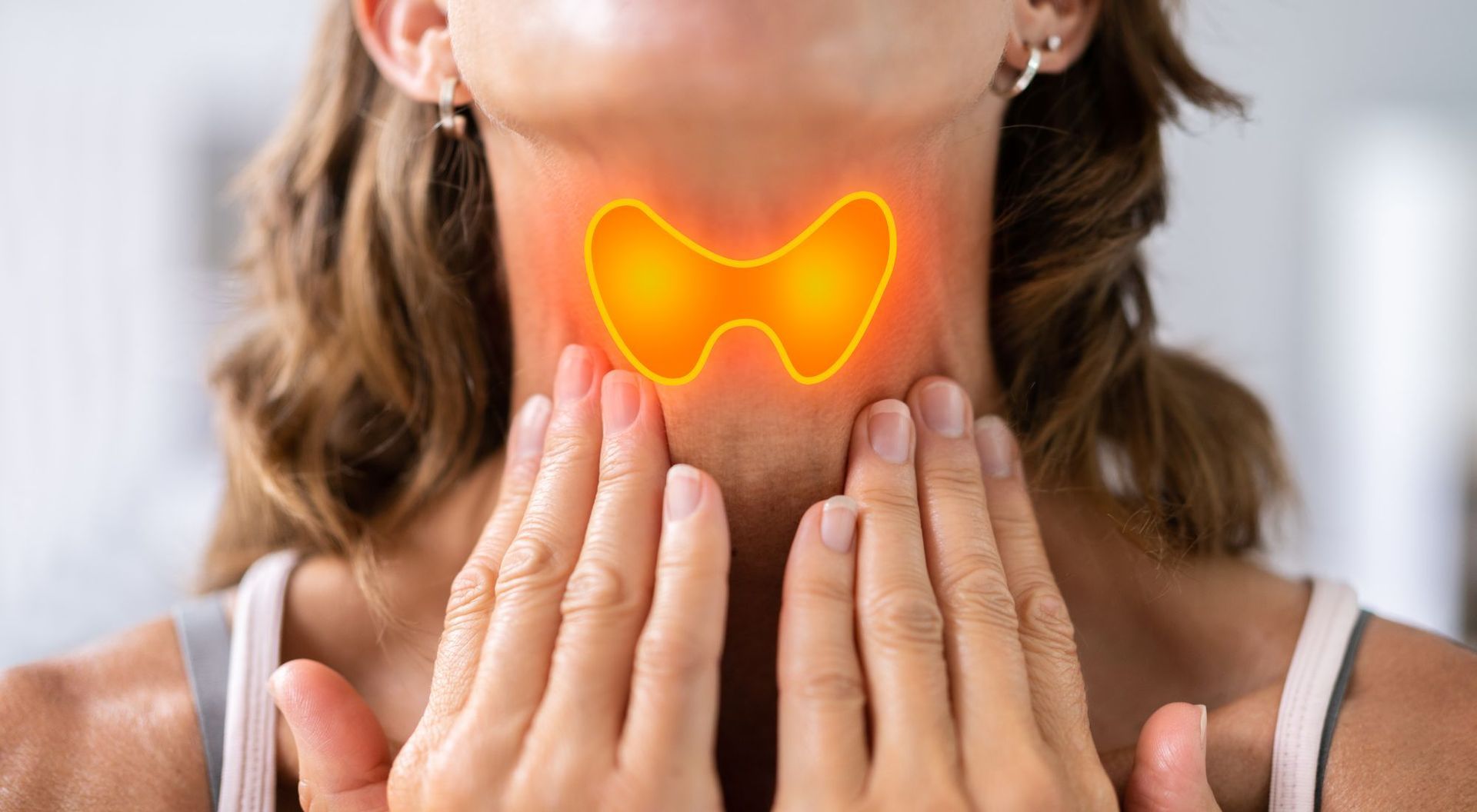
12 Supplements for Hypothyroidism: Manage Symptoms With a Natural Approach
Do you want to minimize the number of synthetic substances and interventions your body is exposed to? You may take thyroid medication, and that’s not as natural as you’d have hoped, but that doesn’t have to break your attempts to be as natural as possible.
You can still address your hypothyroidism symptoms with a wholesome approach centered around getting adequate amounts of the best nutrients for thyroid health.
HealthierU explains how taking any one of these 12 important supplements may help support the thyroid and your overall health. We show you where to find them in food, and how to determine whether you need supplementation.
Table of Contents
What Is the Best Supplement for Hypothyroidism?
There is no single supplement that improves all aspects of thyroid health. Rather, it is a conglomeration of vitamins and nutrients that promote optimal thyroid function.
HealthierU can help you figure out which ones are most needed for you, based on your unique health situation.
The 12 Best Supplements for Hypothyroidism
Although it is best to get nutrients from your diet, it’s not always feasible. When it is difficult to get adequate amounts of a given nutrient from the food you eat, supplementation can help.
#1: Iodine
An essential nutrient for the synthesis of thyroid hormone in the body, iodine is found in many foods, though mainly in fish and marine plants. The recommended daily amount of iodine necessary to sustain proper thyroid hormone levels is 150 micrograms for adults.
Without enough iodine, the thyroid cannot produce adequate amounts of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), both of which contain iodine. A deficiency of iodine may lead to hypothyroidism. Chronically low thyroid hormone levels cause the continuous secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which overstimulates the thyroid and may cause enlargement.
While blood levels of iodine must be sufficient, an excess of the mineral may also lead to complications, so your iodine concentration must be monitored carefully through blood tests.
#2: Vitamin B
Several of the B vitamins play an important role in thyroid health:
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) may help remedy thyroid fatigue and ensure the adequate release of stomach acid for the digestion of fats and proteins.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) may help soothe symptoms of Hashimoto’s disease, one of the major causes of hypothyroidism.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) doesn’t appear to improve thyroid function directly, but it may have a positive influence on gut motility and immune function.
- Vitamin B12 doesn’t have a clear role, but there is an association between B12 deficiency and hypothyroidism, though not all hypothyroid patients exhibit the deficiency. This study reports an improvement in hypothyroid symptoms following supplementation with B12.
#3: Selenium
Selenium is a component of several proteins that are critical for thyroid function:
- Thyroid glutathione peroxidase is responsible for preventing oxidative damage to the thyroid. In cases of selenium deficiency, this enzyme cannot perform its normal function, resulting in necrosis, which draws chronic inflammation to the area and damages the thyroid.
- Deiodinases are responsible for the synthesis and metabolism of thyroid hormones. Three types of deiodinases are involved in the conversion of one kind of thyroid hormone to another at appropriate times.
Selenium’s antioxidant properties may also contribute to the improvement of symptoms caused by autoimmune thyroiditis in selenium-deficient patients.
#4: Zinc
While zinc’s role in thyroid hormone synthesis and metabolism is not clearly understood, it appears to work as a cofactor in the same processes of conversion that the deiodinases are involved in. Zinc supplementation may help to increase thyroid hormone levels.
Some symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as
hair loss, may not improve with thyroid hormone replacement alone but require zinc supplementation as well.
#5: Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency may be linked to the development of autoimmune thyroid disorders. Although the exact molecular mechanism of this connection is unknown, supplementation with
vitamin D may result in a decrease of thyroid antibodies, thus protecting the thyroid from further damage caused by Hashimoto’s disease.
#6: Tyrosine
Tyrosine is an essential amino acid that is the precursor to many molecules important in human physiology, including the thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormone production occurs via the following steps:
- Thyroglobulin is a large protein with tyrosine residues, which serve as the attachment sites for iodine atoms. This attachment turns the protein into monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT), depending on how many atoms are bound.
- MIT and DIT combine to form triiodothyronine (T3). Two DIT molecules combined make T4. These are the thyroid hormones.
Because of its central role in thyroid hormone production, tyrosine is often included in supplements that support thyroid health.
#7: Calcium
The thyroid gland’s parafollicular cells produce calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate blood levels of calcium and inhibit bone resorption. Thyroid disorders disrupt the production of calcitonin as well as that of thyroid hormones, possibly leading to irregular blood levels of calcium and detriment to the bones.
Hypothyroid patients must take care to ensure their calcium levels are adequate. It should be noted, however, that calcium can interfere with the absorption of levothyroxine, the synthetic form of thyroid hormone. Therefore, calcium supplements should be taken at least four hours before or after taking levothyroxine.
#8: Carnitine
Carnitine is another essential amino acid, found mainly in red meat, and is most beneficial for skeletal muscles. Low levels of
muscle carnitine have been associated with both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. For hypothyroid patients suffering from muscle soreness and
fatigue, carnitine supplementation may be especially helpful.
#9: Ginger
Some symptoms of hypothyroidism persist even when the condition is controlled by thyroid hormone replacement. A 2022 study found that ginger supplementation has proven beneficial for many hypothyroid patients by relieving the following symptoms:
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Brain fog
- Memory loss
Beyond just relieving these symptoms, the same study identified an improvement in lipid profile and weight loss/regulation in the patients tested after supplementing with ginger for a month.
#10: Iron
Not only do iron deficiency and hypothyroidism share many of the same symptoms (such as fatigue, hair loss, muscle weakness, or brain fog), but they are also comorbid conditions. Hypothyroidism impairs iron absorption and decreases the production of the protein that stores iron in the blood.
Iron deficiency, in turn, may reduce the function of thyroid peroxidase (responsible for thyroid hormone synthesis) and the binding of T3 to its receptor site. Furthermore, by triggering inflammation in the thyroid, iron deficiency is another culprit in the development of autoimmune thyroid disorders.
Even when it is hard to determine the primary cause (iron deficiency or hypothyroidism) of certain symptoms, iron
supplementation may help to resolve them.

#11: Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency can negatively affect thyroid health by:
- Disrupting the conversion of T4 to the active form T3
- Increasing one’s risk of developing an autoimmune thyroid disease
- Interfering with the regulation of TSH levels
There are several supplement preparations available containing magnesium, but they differ in quality. Some forms, such as magnesium glycinate and magnesium
citrate, have greater bioavailability, meaning your body is better able to absorb and use them.
#12: Vitamin A
This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.
Food Supplements for Hypothyroidism
The best approach to diet for people struggling with the symptoms of hypothyroidism does not involve extreme or fad diets. Eating a variety of foods rich in the essential nutrients discussed above will have a positive effect on your overall health as well as on your thyroid in particular.
Consult this list for common food sources of each nutrient, but discuss with your healthcare provider 1) the possibility of overconsumption of nutrients that might be counterproductive in your case, and 2) the necessity of supplementation.
| Nutrient | Food Sources |
|---|---|
| Iodine | Seaweed, cod, tuna, shrimp, dairy, eggs, lima beans |
| B vitamins | Salmon, leafy greens, liver, eggs, milk, beef, poultry, yogurt |
| Selenium | Brazil nuts, fish, ham, grains, poultry, cottage cheese, eggs, brown rice |
| Zinc | Oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, oats |
| Vitamin D | Fatty fish, dairy, and some mushrooms |
| Tyrosine | Lean meat, nuts and seeds, soy beans |
| Carnitine | Red meat, poultry, fish, dairy |
| Ginger | Asian or Indian cuisine, ginger tea |
| Calcium | Dairy products, leafy greens, sardines, salmon |
| Iron | Oysters, leafy greens, lean meats, squash, pumpkin seeds |
| Magnesium | Whole grains, legumes, avocados, nuts and seeds, leafy greens, dark chocolate |
| Vitamin A | Dark, leafy greens, orange and yellow fruits and vegetables |
How Do I Know If I Should Start Taking Thyroid Supplements?
Generally speaking, a diet with a good variety of nutrient-dense foods provides adequate amounts of the nutrients that support thyroid health, but every patient is different in terms of:
- Nutrient absorption
- Underlying circumstances that affect how the body responds to different substances
- Dietary needs
For this reason, supplements for hypothyroidism can be dangerous if not taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can monitor your blood levels of the various nutrients and warn you of any contraindications.
HealthierU can request the right exams to evaluate your body’s needs and create a list of supplements that are most likely to make a positive difference in your experience with hypothyroidism.
HealthierU: Manage Hypothyroidism Symptoms With a Natural Supplementation Approach
If you are looking for natural treatment for hypothyroidism, look no further than HealthierU, founded by Dr. Donna Sergi, a holistic nutritionist and chiropractor who specializes in women’s health and wellness. For nearly three decades, Dr. Sergi has served clients in the Brooklyn area, helping them find safer, more natural ways to address their health issues.
Whatever you are struggling with — hormonal imbalances, digestive issues, hair loss, acid reflux, acne, constipation, lower back pain, or something else — HealthierU can help you achieve more optimal health and a greater sense of wellness.
By following HealthierU’s comprehensive and personalized guidance, you can develop dietary and lifestyle habits that have a positive and lasting impact on your thyroid health.