ALT, AST, and Hypothyroidism: Understanding the Thyroid–Liver Connection
You find yourself worn out almost all the time. Your brain feels foggy, and sometimes it is hard to concentrate and remember things. You’ve gained weight unexpectedly. It can feel like your body has turned against you.
You might be suffering from hypothyroidism.
Living with hypothyroidism can affect your energy, weight, and mood. But did you know that an underactive thyroid can mean your liver is unhealthy, too?
We often think of the liver and thyroid as totally independent systems, but the reality is, they are more connected than we realize. The liver and the thyroid depend on one another to function properly.
In this article, we will explore the link between hypothyroidism and liver health and what you can do to support both.
Table of Contents
What Is the Link Between Hypothyroidism and the Liver?
The liver and the thyroid are intimately connected. The interactions of the thyroid and liver hormones are essential for maintaining homeostasis, or a stable internal environment, in your body.
The liver depends on thyroid hormones to perform its metabolic functions. Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, means that your body is not producing enough thyroid hormones. The link between the liver and the thyroid signifies that with the absence of adequate thyroid hormones, the liver can begin to dysfunction.
Hypothyroidism and high liver enzymes have been connected to several liver diseases, including:
- Abnormal lipid metabolism: With this condition, lipid levels (cholesterol and fat) in the blood are outside of the healthy range, either elevated or low.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This disease is characterized by fat building up in the liver of people who do not consume alcoholic beverages.
- Hypothyroidism-induced myopathy: This condition presents as muscle weakness, fatigue, and pain caused by an underactive thyroid and impacts liver function.
- Hypothyroidism-associated gallstones: There is an increased risk of cholesterol gallstones in individuals without enough thyroid hormones.
What ALT and AST Levels Reveal About Your Liver Health
Liver enzymes are essential for a healthy, functioning liver.
The enzymes help the body by:
- Metabolizing medications and nutrients
- Aiding in digestion
- Maintaining blood sugar levels
- Producing cholesterol
- Regulating hormones
Liver enzyme levels are indicators of overall liver health.
If enzyme levels are elevated, it could be a sign of liver problems. Two of the most commonly measured liver enzymes in the blood are alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
ALT Enzymes
Alanine transaminase (ALT) is an enzyme that is mainly found in the liver. It converts proteins into energy for liver cells. Typically, ALT levels are low; however, if the liver is damaged or inflamed, ALT enzymes may be released into the bloodstream, elevating ALT levels on blood tests.
Normal levels are considered between 4 and 36 U/L. When ALT levels are elevated, it can be an indication of liver injury or disease.
Common causes of elevated ALT are:
- Hepatitis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain medications
- Some muscle disorders
ALT levels can vary among individuals and don’t always indicate a serious problem.
AST Enzymes
AST enzymes are found in essential organs like the heart, muscles, kidneys, and brain, with the highest concentration found in the liver. It is usually measured in blood tests to determine liver health or potential liver injuries.
AST is a protein that helps process amino acids, which allows the body to carry out metabolic functions like generating energy.
The normal range for AST is 8-33 U/L.
Whenever AST levels are
elevated, it could be an indication that tissue is damaged in the body, often in the liver. However, high levels may not be an indication that something serious is wrong.
Can Hypothyroidism Cause Elevated ALT and AST?
Does hypothyroidism cause elevated liver enzymes?
Yes, ALT and AST can be elevated in patients with hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism may cause the liver to be unable to effectively process and clear fats. This impairment leads to an accumulation of fat in the liver. Excess fat in the liver triggers inflammation.
When the thyroid doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones and fat builds up in the liver, the liver then begins releasing ALT and AST into the bloodstream, elevating these enzyme levels.
Potential Effects of Hypothyroidism on The Liver and Its Enzymes
What is the connection between elevated liver enzymes and hypothyroidism?
Liver enzymes like ALT and AST are not directly related to thyroid function. However, hypothyroidism can cause this secondary effect on the liver. Let’s explore potential reasons why.
Liver Functionality
Optimal metabolic function and overall liver health are dependent on thyroid hormones. When these hormones are out of balance, the liver cannot function correctly.
Without adequate thyroid hormones, the liver cannot manage the breakdown of cholesterol and triglycerides. In turn, cholesterol and triglycerides cannot be effectively removed from the bloodstream, and they will build up in the body.
This may result in:
- Fatty Liver Disease: Fat may accumulate and contribute to liver inflammation and damage.
- Atherosclerosis: Fats may accumulate in the bloodstream, and plaque may form on artery walls, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart disease and heart attack.
- Hepatic Lipase Deficiency: This causes an imbalance of cholesterol and triglycerides and can lead to atherosclerosis.
Liver Metabolism
Liver metabolism slows down in patients with hypothyroidism, affecting the way the liver processes fats and enzymes.
When liver metabolism slows, it can lead to a host of problems, including:
- Impaired ability to remove toxins from the blood
- Changes in the effectiveness of drug metabolism and increased side effects
- Disruption of nutrient absorption and use
- Increased fluid retention
- Hormonal imbalances
- Increased risk of infections
Muscle Involvement
Although AST and ALT enzymes are found primarily in the liver, they are also found in the muscles. When the enzymes are released in the bloodstream at elevated levels due to hypothyroidism, muscle breakdown (myopathy) may occur.
Thyroid hormones are necessary for many aspects of muscle function, including energy production, metabolism, and muscle fiber structure. The symptoms can manifest as pain, weakness, stiffness, or cramps.

Potential Complications of Untreated Thyroid and Liver Issues
Can hypothyroidism cause elevated liver enzymes? Yes. When hypothyroidism and other liver problems associated with elevated enzymes are left unchecked, several complications could happen.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are serious complications that can occur when fat builds up in the liver. The liver becomes swollen and damaged from fat deposits, similar to what happens with heavy alcohol use. These diseases may lead to scarring, cirrhosis, or liver cancer if untreated.
Liver dysfunction may also affect thyroid hormone levels and metabolism. Hormonal imbalance may result in a goiter, an enlargement of the thyroid, in an attempt to produce more hormones. Getting thyroid hormones under control is beneficial for liver health.
Untreated hypothyroidism may also lead to cardiovascular issues because of the increase in cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart disease.
If caught early enough, these complications are reversible if hypothyroidism gets under control.
At HealthierU, our goal is to help you achieve hormonal balance naturally. Request a nutrition consultation today to take the first step in healing.
6 Steps To Support Liver Health With Hypothyroidism
#1: Take Your Thyroid Medication as Prescribed
One step toward treating hypothyroidism is medication. The medication is designed to replace the thyroid hormones that the thyroid is having difficulty producing on its own.
Taking medication as prescribed by a doctor keeps the body’s functions from slowing down and keeps hormone levels in the normal range.
Keeping hormone levels in the appropriate range alleviates symptoms of hypothyroidism, including fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, and cold intolerance. It also prevents damage to the liver.
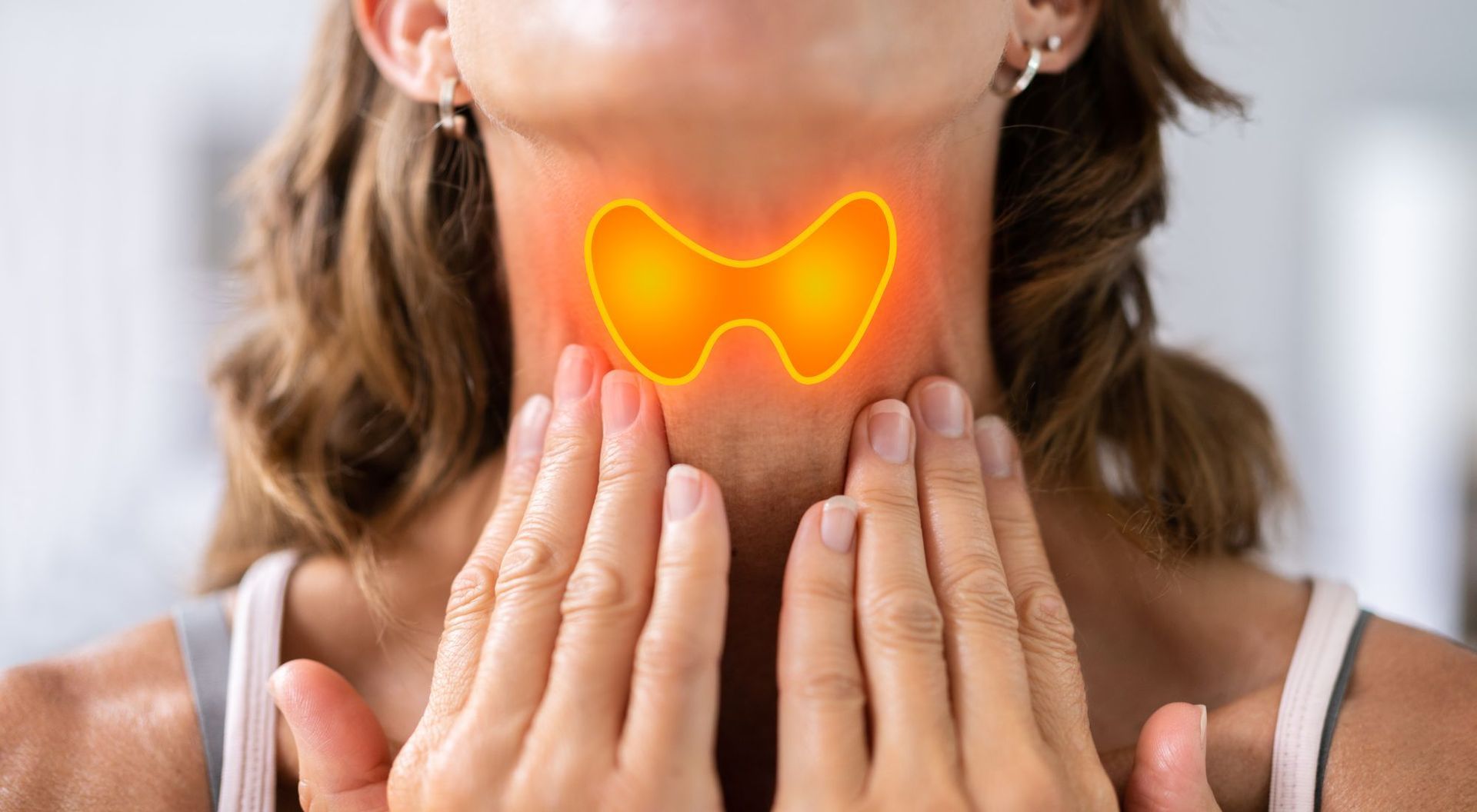
#2: Follow Up Regularly With Your Doctor
To maintain a healthy hormonal balance and keep hypothyroidism from getting out of hand, it is essential to maintain regular follow-up appointments with the doctor.
It is especially necessary to have follow-up appointments with the doctor when a medication has been prescribed or changed to ensure that the medication is working effectively. Whenever the dosage has changed, follow-up should happen within 6-8 weeks.
The goal of treatment is to keep thyroid hormones in balance.
Follow up with the doctor sooner if:
- You experience a return or worsening of symptoms
- You gain or lose weight (10 pounds or more)
- You start or stop taking medication that can interfere with your thyroid medication
- You start or stop taking medication for seizures
- You want to stop treatment
#3: Avoid Alcohol
Individuals with hypothyroidism are already at greater risk of developing liver problems due to the interconnectedness of the thyroid and the liver.
Adding alcohol to the mix may increase the risk of developing fatty deposits in the liver.
Excessive build-up of fat in the liver can cause inflammation and disease, in addition to normal tissue being replaced by scarred tissue. Symptoms may progress significantly before damage to the liver is detected.
#4: Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing weight has a positive effect on improving non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in both normal-weight and overweight people.
Weight loss is usually accompanied by increased activity; therefore, losing weight typically results in improvement of:
- Liver enzymes
- Histology
- Serum insulin levels
- Quality of life
Making healthy lifestyle choices is beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight and improving thyroid and liver issues.
#5: Stay Active
This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.
#6: Eat a Balanced, Nutritious Diet
The thyroid gland requires specific nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc to function properly. However, it is important not to have excessive intake of these nutrients either as they can harm thyroid health in large quantities.
Leafy vegetables, fiber, and healthy fats support liver function and reduce inflammation. Consuming these foods is essential for managing or preventing damage and disease.
To support both liver and thyroid functions, it is important to have a balanced diet that is rich in whole, unprocessed foods such as fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
A balanced diet, along with portion control, can assist in weight management, which directly affects liver and thyroid health.
At HealthierU, Dr. Sergi works to determine the cause of your symptoms and address them naturally without the use of traditional medication. A customized plan with
nutritional support and lifestyle guidance can help you solve your health concerns.
Get Expert Help Managing Hypothyroidism and Elevated Liver Enzymes With HealthierU
High TSH levels can affect nearly every part of your body by slowing down your body’s functions. Effects of high TSH include:
- Fatigue and low energy
- Weight gain
- Cold sensitivity
- Cognitive issues
- Cardiovascular effects
- Menstrual irregularities
- Skin and hair changes
- Muscle and joint problems
Thyroid problems can be treated, but if left untreated, they can cause serious issues — including heart problems, nerve damage, and infertility.
Dr. Sergi of HealthierU offers a holistic nutritional approach to thyroid health. Her decades of experience and desire to help people solve their health problems in a natural, non-toxic way help put you on the path to resolving your thyroid issues.



