How To Reduce Gut Inflammation the Healthy Way
"The content below is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition."
You’re struggling with a variety of random symptoms — nausea and constipation keeps you up at night, fatigue makes it difficult to function throughout the day, and the bloating is uncomfortable.
No matter what you do, the symptoms don’t go away.
Are you tired of unsuccessfully treating these symptoms and not understanding what is causing them? Too often, we become accustomed to managing symptoms of an underlying illness instead of looking further into why we might be repeatedly experiencing the same symptoms.
If you think inflammation of the gut is to blame for your various health issues, there are steps you can take to get rid of these symptoms.
Table of Contents
What Triggers Inflammation in the Gut?
The majority of our immune system resides in the gut microbiome and protects us from invaders by telling apart our cells from those belonging to others.
When the immune system believes the body is being invaded, it mounts an immune response. Occasionally, this immune response occurs due to food and environmental chemicals.
What Are the Effects of Gut Inflammation?
Continuous immune attacks can lead to inflammation, decreasing your ability to absorb nutrients. As a result of the inflammation, your gut microbiome is unable to effectively run your metabolism, and your digestive health is affected.
“Dysbiosis” results from an imbalanced microbiome and can manifest in many ways.
A few symptoms of dysbiosis include:
- Colitis
- Diarrhea
- Gas
- Constipation; or
- Signs of irritable bowel syndrome
The microbiome can also show other symptoms that are less obvious in the gut, like:
- Joint pain
- Headaches
- Skin rash; and
- Inability to focus
Other Health Risks Caused by Inflammatory Foods
Excess inflammation is also associated with some foods related to chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
This is not surprising since inflammation plays a crucial role in developing these diseases.
Are you experiencing digestive health issues and want to know what is causing them? Having a healthy digestive system is not only essential for your overall well-being, but poor digestive health can cause many health problems.
Our number one goal at HealthierU is to get you feeling better again. To determine which organs are not functioning correctly and causing your symptoms, we use Nutrition Response Testing, a proven and non-invasive method.
To learn more, contact us today.
What Foods Cause Gut Inflammation?
Inflammatory foods include:
- Simple and refined sugars (high glycemic carbohydrates)
- Unhealthy fats
- Ultra-processed foods
- Charred foods
- Excessive alcohol
- Conventional corn-fed meat
- Processed food chemicals; and
- Artificial sweeteners
Consuming simple and refined sugars contributes significantly to increased inflammation in the body. Avoid sugars like:
- White sugar
- Sodas
- Candies
- Juice
- Syrups
- White bread
- High-sugar cereals; and
- High-fructose corn syrup
Among the unhealthy fats are trans fats, which are found primarily in ultra-processed foods, such as:
- Crackers
- Baked goods; and
- Chips
Limiting your intake of charred foods is also recommended due to their pro-inflammatory properties.
When it comes to meat and dairy products, they are affected by what the animal eats. For example, meat and dairy raised on corn are considered pro-inflammatory, while grass-fed and organic meat and dairy are much healthier, especially red meat.
There is also some evidence that shows certain processed foods may be pro-inflammatory, including:
- Polysorbate 80
- Carrageenan; and
- Artificial sweeteners
8 Best Ways To Reduce Inflammation in the Gut
#1: Follow an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
It is essential to follow an anti-inflammatory diet, but what is included in this type of diet?
Currently, there are no widely accepted definitions of an anti-inflammatory diet, but three examples include:
- Plant-based diets — It is essential to consume proper portions of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, protein, and healthy fats to have a balanced and healthy plant-based diet.
- Mediterranean diets — Mediterranean diets are rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, beans, nuts, and seeds. Additionally, olive oil is a primary source of fat, and a low to moderate amount of dairy products, such as eggs, fish, and poultry, should be consumed.
- Okinawan diets — Along with small amounts of fish, the Okinawa diet consists mainly of vegetables and soy.
To
reduce inflammation in the gut, adding more anti-inflammatory foods to your diet could be a great place to start since there are so many options on what you might eat. Rather than eating perfectly, the goal should be to consume anti-inflammatory foods more often.
Examples of Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Luckily, anti-inflammatory foods are abundant and probably simple to work into your diet:
1. Consuming more vegetables and fruits is a great way to eat more polyphenols, which have been shown to reduce inflammatory markers in the blood.
2. Turmeric and ginger, both anti-inflammatory spices, can be eaten fresh or powdered. Add black pepper to turmeric to increase the bioavailability and effectiveness of turmeric, as black pepper contains a substance called piperine.
3. Choose plant-based proteins, including:
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Black beans
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Asparagus
- Edamame
- Tofu; and
- Tempeh
4. Choose from the following anti-inflammatory fats:
- Extra-virgin olive oil
- Avocado oil
- Walnut oil
- Hemp oil
- Flaxseed oil
- Avocadoes
- Hemp hearts
- Chia seeds; and
- Omega-3 fats
5. Look for carbohydrates that are high in fiber and low in glycemic index and can be found in whole grains, such as:
- Rye
- Barley
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Brown rice; and
- Teff
The options are plentiful, as you can see!
#2: Try an Elimination Diet
If you suspect certain foods are triggering inflammation in your gut, begin removing the likely culprits for roughly two to three weeks at a time.
In these diets, the foods most commonly excluded are:
- Dairy
- Gluten
- Sugar
- Nightshades
- Soy
- Alcohol; and
- Processed foods
While you are not consuming these specific foods, you can note any changes you see. You should then slowly reintroduce these foods back into your diet over two to three days while noting any specific symptoms that might occur.
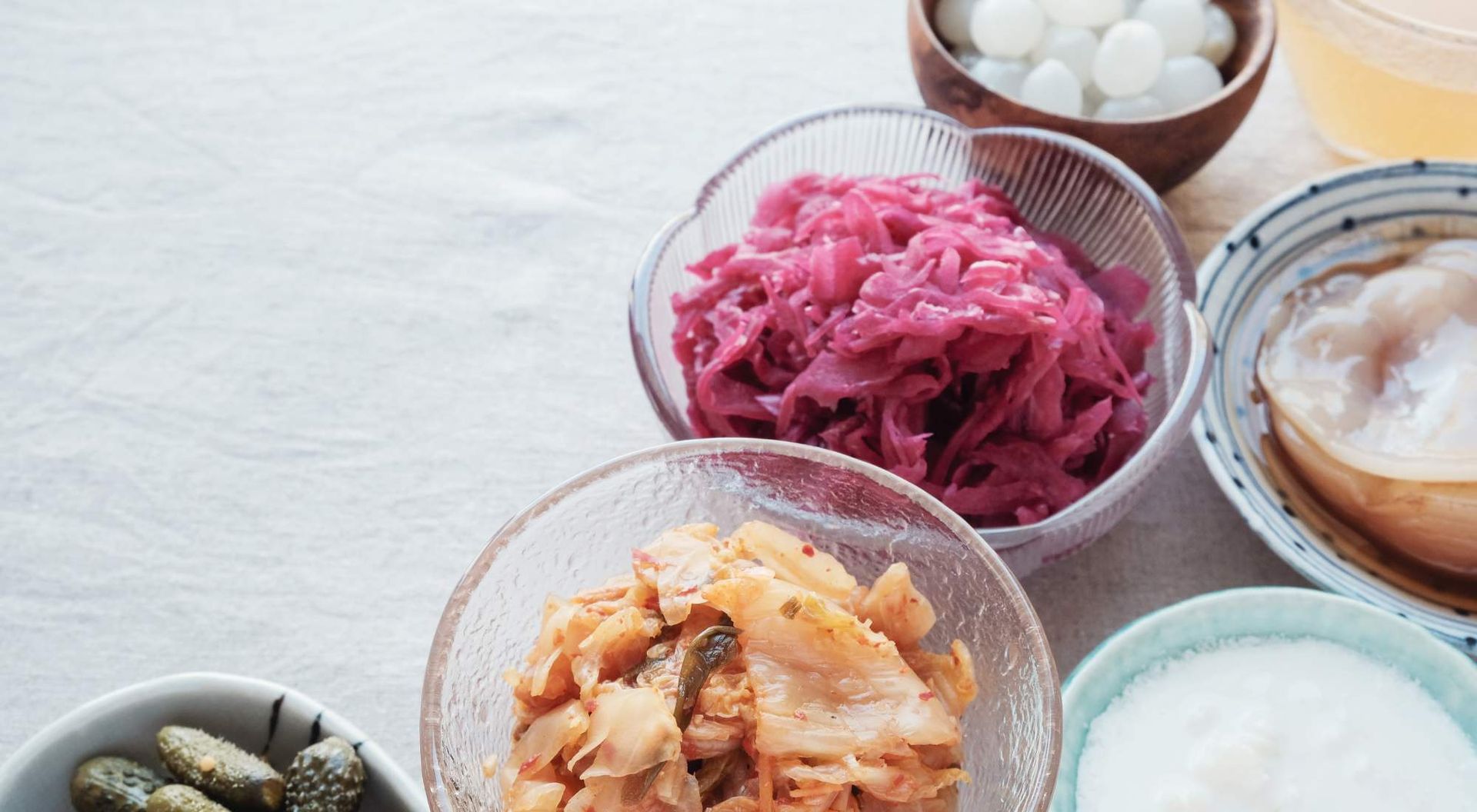
#3: Eat Probiotic Foods To Boost Gut Health
Eating probiotic foods provides your gut with live bacteria that support your health. With their health-boosting microorganisms, probiotics can significantly improve your immune system.
Foods rich in probiotics include:
- Low- or no-sugar yogurts and kefirs with live, active cultures
- Fermented pickles
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Kombucha; and
- Apple cider vinegar
Probiotic supplements can help, but for maximal effect, they need to get through your stomach acid and reach your colon, where beneficial bacteria live. Unfortunately, many probiotic supplements do not get through your stomach acid; because of this, probiotics are best delivered to your body through food because of how it is digested and absorbed.
While the American diet often does not include many fermented foods, they offer robust support for your body. If you are not a fan of fermented foods, find a food rich in probiotics you are willing to have. A popular option is Greek yogurt with no sugar. Then, to help with the taste, mix in some tasty additions, like frozen berries and ground flax seeds, which are prebiotics.
As well as producing B12 and K vitamins, probiotics also prevent harmful bacteria from spreading throughout your body.
#4: Fuel a Healthy Gut With Prebiotics
Your gut's healthy microbes are fuelled by prebiotics, which acts as fuel for probiotics.
For probiotics to function correctly in the gut, prebiotics are used to provide them with sustenance. This allows them to stick to the bowel wall and thrive in the gut.
Abundant sources of prebiotics include:
- Bananas
- Dandelion greens
- Garlic
- Onion
- Chicory root
- Flax seeds
- Chia seeds
- Legumes
- Whole grains; and
- Vegetables such as asparagus and artichokes
#5: Work To Reduce Stress Levels
Stress can affect the microbiome.
Due to the vagus nerve —the body's longest nerve —the gut microbiome is directly connected to the brain. Like environmental toxins, high-stress levels block the vagus nerve's function. Because of this connection, constant stress can lead to a poorly functioning gut.
You can combat this by finding activities that can help you relax, even for just a few moments, including:
- Meditation
- Mindfulness
- Going for a walk
- Taking a bubble bath; and
- Deep breathing techniques
#6: Stay Active
Not only can exercise support a healthy weight, but it can also support your gut health. Research has shown that a person's microbiome is positively impacted by their activity level.
Despite what many might believe, it is possible to improve your well-being through gentle exercises such as:
- Walking
- Cycling
- Yoga; and
- Swimming
#7: Don’t Vape
There has been evidence that e-cigarettes and vaping damage the gut.
As a result of heating and vaporizing the e-cigarette liquid, the ingredients change into damaging compounds. By damaging the gut lining, the gut becomes more susceptible to infections and has increased inflammation.
The act of vaping may seem like a healthy alternative to smoking cigarettes, but it may have a detrimental effect on the gut, increasing inflammation and making the body more susceptible to infections.
#8: Try Nutrition Response Testing
Nutrition Response Testing is a noninvasive test used to identify underlying health problems in the body.
As we have discussed, your body needs critical nutrients to fight inflammation, such as:
- B-vitamins
- Omega-3 fats
- Vitamin D; and
- Magnesium
Find out if your body lacks any specific nutrients by getting tested.
Using Nutrition Response Testing, HealthierU finds the cause of many symptoms and treats them without traditional medications.
It may be time for you to consider Nutrition Response Testing if you have not been feeling well lately and suspect your gut might be to blame.
To learn more, contact us today.
HealthierU May Be Able To Help Reduce Your Gut Inflammation
Have you decided that the symptoms you are experiencing might be a result of gut inflammation? If so, HealtheirU can help.
The relationship between nutrition and gut health is well understood, and by using natural remedies, we help you identify and resolve gut issues.
Dr. Donna Sergi specializes in women's health and wellness and listens to your concerns. You are not just a number to us.
If you would like to learn more about our services, please feel free to contact us.