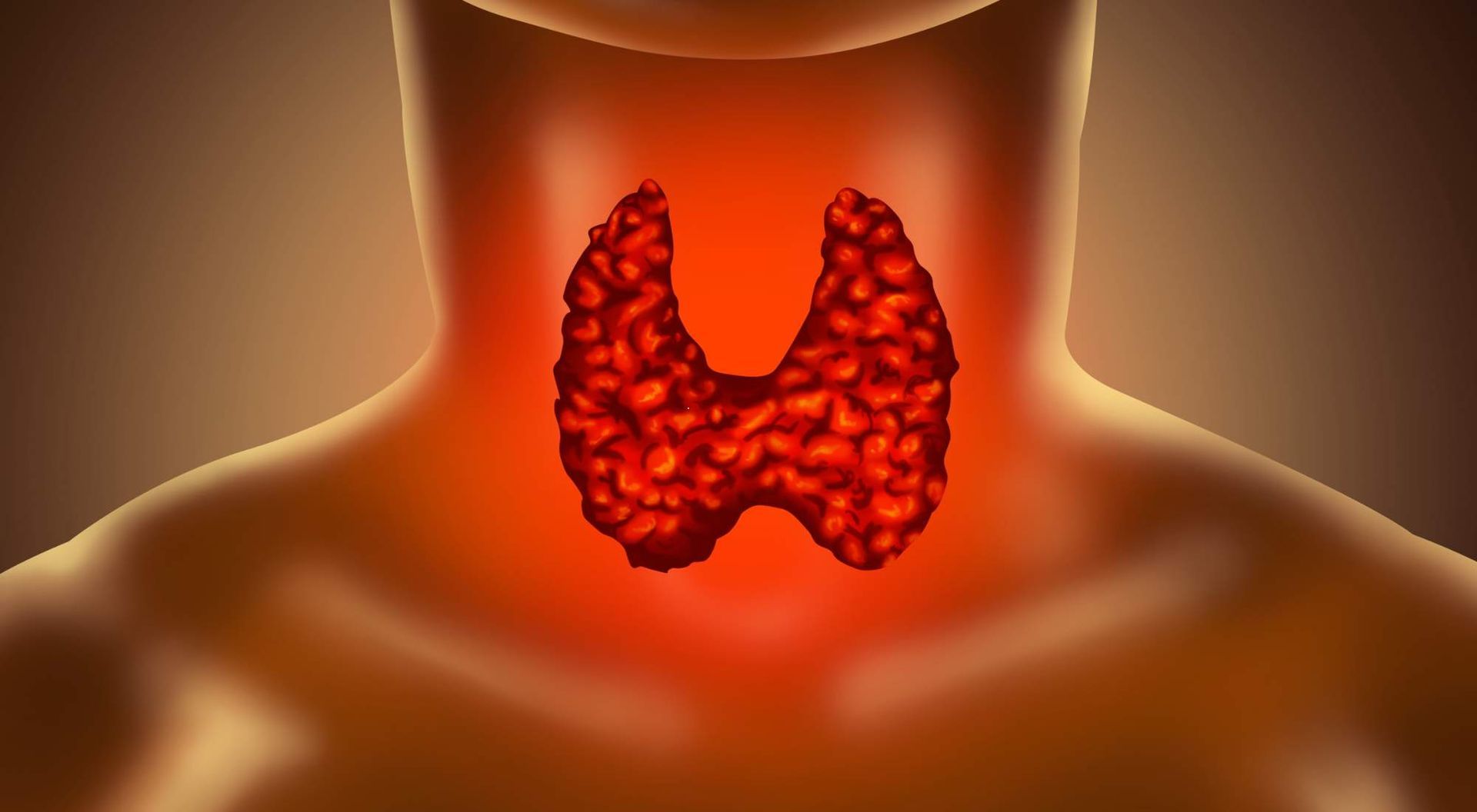
Can Pregnancy Cause Thyroid Issues? The Intersection of Hypothyroidism and Pregnancy
"The content below is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition."
Whether this is your first pregnancy or your fifth, you are probably becoming familiar with the common symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Hair and skin changes
- Swelling
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- And more
But these symptoms also mimic those that come with hypothyroidism, and you may be asking the question, “Can pregnancy cause hypothyroidism?”
Among all the other changes your body experiences during pregnancy, thyroid function change may be one of them.
In this guide, we’ll help you know how to recognize hypothyroidism during pregnancy and answer some common questions about how hypothyroidism is diagnosed and treated in expectant mothers.
Table of Contents
Can Pregnancy Cause Hypothyroidism?
Pregnancy causes many changes in a woman’s body.
Hormone changes in pregnancy can be responsible for the start of hypothyroidism or can make hypothyroidism symptoms worse for women who are diagnosed with the disease before becoming pregnant.
The American Thyroid Association asserts that “pregnancy has a profound effect on thyroid gland function,” making thyroid disease common in pregnancy. According to the
2017
Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and Postpartum, hypothyroidism occurs in two to three out of every 100 pregnancies.
Why Does Pregnancy Cause Thyroid Problems?
A woman’s body experiences vast
hormonal changes during pregnancy, which can be a main factor in thyroid function changes in pregnant women. Changes in the thyroid itself — increase in size — can also contribute to a woman’s likelihood of developing hypothyroidism during pregnancy.
Hormonal Changes
Two main hormones contribute to changes in thyroid function during pregnancy:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Estrogen
In the first trimester, high hCG levels can stimulate the thyroid, resulting in a low thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). This happens when thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are increased, which, in turn, slows down the production of TSH. After the first trimester, TSH may return to normal for the rest of the pregnancy.
Estrogen may also play a role in causing higher thyroid hormone levels. The amount of thyroid hormone-binding proteins is increased due to estrogen, which results in an increase in total thyroid hormone levels.
Thyroid Changes
In addition to these two hormone fluctuations, changes in the thyroid organ itself can also contribute to hypothyroidism during pregnancy.
The thyroid gland can become enlarged in pregnancy, but the increase in size may not be large enough to be noticed during a physical examination.
However, if significant enlargement of the thyroid gland occurs, a doctor may notice it during a physical examination and order other tests to determine thyroid function and the possibility of the development of hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy
The symptoms of hypothyroidism in pregnant women are often the same as others who have been diagnosed with an underactive thyroid. These symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Muscle cramps
- Constipation
- Concentration problems or mental fogginess
- Extreme tiredness
- Hoarse/scratchy voice
- Swelling
- Weight gain
- Skin and hair changes
- Hand tingling or pain
- Slow heart rate
If a woman is experiencing mild hypothyroidism, she may not experience any noticeable symptoms.
Commonly Asked Questions About Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy
If you’re experiencing some of these symptoms or have already been diagnosed with hypothyroidism, you probably have lots of questions about how hypothyroidism can affect you and your baby during your pregnancy and how it can be treated.
The following frequently asked questions can help educate you and give you some peace of mind as you navigate this potential complication of your pregnancy.
Can You Develop Thyroid Problems During Pregnancy?
Yes, women may develop thyroid problems and symptoms during pregnancy due to the complex changes in the thyroid gland and changes in hormones like hCG and estrogen.
These changes in hormones are most significant during the first trimester. In some pregnant women, thyroid levels may return to normal during the second and third trimesters, but other women may experience hypothyroidism and need thyroid treatment for the duration of their pregnancy.
What Is the Relationship Between the Thyroid Function of the Mother and their Unborn Baby?
Among other things, the baby relies on the mother for the production of thyroid hormone, especially during the first 18 to 20 weeks of pregnancy. After that, the baby begins producing its own thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones are necessary for the development of a baby’s brain and nervous system.
Even after beginning to produce its own thyroid hormones, the baby will remain dependent on its mother to receive sufficient amounts of iodine — a mineral that is needed to produce the thyroid hormones.
The World Health Organization recommends iodine supplementation of 250 micrograms per day during pregnancy to aid in thyroid hormone production.
At HealthierU, Dr. Sergi’s priority is to offer holistic nutrition and supplementation assistance to each of her patients, including expecting mothers. If you’ve been diagnosed with hypothyroidism before or during your pregnancy, Dr. Sergi will work with you to develop a nutritional plan designed to meet your specific needs.
Request a free consultation and get started on your journey to holistic health.
What Complications Can Occur With Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy?
Hypothyroidism that goes undiagnosed or untreated in pregnancy can lead to significant complications for both the mother and the baby. If you feel like you are experiencing any signs of an underactive thyroid, don’t be afraid to mention it to your healthcare professional. Be your own advocate and begin the conversation with your doctor to improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy for you and your baby.
How Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy May Affect the Mother
Women with mild hypothyroidism may not experience significant symptoms, but those with severe forms of hypothyroidism may be at risk for these more serious complications:
- Risk of miscarriage
- Congestive heart failure
- Anemia
- Muscle pain and/or weakness
- Pre-eclampsia
- Postpartum bleeding
- Abnormalities of the placenta
How Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy May Affect the Unborn Baby
Because the baby is completely dependent on the mother for thyroid hormones during the first trimester, a mom’s unhealthy functioning thyroid can have harmful effects on the baby both during pregnancy and after delivery.
Because thyroid hormone is essential for the baby’s brain development, many of the complications due to a low-functioning thyroid may be neurological in nature.
Untreated hypothyroidism during pregnancy may result in the following complications for the baby:
- Impaired brain development
- Low birth weight
- Stillbirth
- Congestive heart failure
- Low IQ
- Problems with development
Congenital hypothyroidism, when the baby’s thyroid doesn’t function at birth, is another condition that has significant complications for the baby. Congenital hypothyroidism is caused when the baby’s thyroid doesn’t develop correctly during pregnancy.
This condition can result in neurological and developmental abnormalities. However, with early treatment, these abnormalities can be treated.
In the United States, all newborns are screened for congenital hypothyroidism so that treatment, if necessary, can begin as soon as possible.
How Is Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy Treated?
Hypothyroid treatment involves replacing the thyroid hormone so the expectant mother has an adequate amount of the hormone for the duration of her pregnancy. This treatment may involve a combination of
hormone replacement and holistic nutrition.
Hormone Replacement
To ensure thyroid hormone levels remain adequate during pregnancy for a hypothyroidism patient, doctors prescribe hormone replacement therapy. Since the thyroid isn’t producing adequate amounts of thyroid hormone, a pregnant woman with hypothyroidism may be prescribed a medication like levothyroxine.
Thyroid levels can fluctuate during pregnancy, so thyroid replacement dosages may also need to change.
Thyroid levels should be monitored regularly during the pregnancy — usually, every four weeks — to ensure hormone levels remain adequate. Some pregnant women with hypothyroidism may need to see their endocrinologist (in addition to their obstetrician) to manage the condition.
After delivery, thyroid hormone levels should continue to be monitored, which may involve decreasing the dosage of medication as necessary.
When taking prenatal vitamins, women taking levothyroxine during pregnancy should be careful not to take them at the same time. Ideally, they should be taken four hours apart to ensure proper absorption of the thyroid hormone.
If you’ve been diagnosed with hypothyroidism before becoming pregnant, it’s important for your doctor to do tests right after you find out you’re pregnant to make sure your hormones are balanced from the beginning of your pregnancy.
Holistic Nutrition
Eating a hypothyroidism diet can also work in conjunction with hormone replacement therapy to ensure proper nutrition for the mother and her developing baby.
Because the thyroid uses large amounts of iodine to function properly, a diet rich in iodine is essential both for the mom and the baby.
Foods that can help manage hypothyroidism during pregnancy include the following:
- Foods rich in iodine (to make thyroid hormone and provide nutrients to the baby when breastfeeding)
- Dairy
- Seafood
- Eggs
- Meat
- Poultry
- Iodized salt
- Food rich in magnesium (helps the thyroid generate hormones in moderation)
- Greens
- Peppers
- Carrots
- Spinach
- Mushrooms
- Foods high in protein (to help strengthen muscles and boost energy)
- Fish
- Eggs
- Meat
- Poultry
- Fruits (to provide antioxidants to support the immune system)
- Berries
- Apples
- Bananas
- Grapes
- Citrus fruit
- Pineapples
- Whole grains (to add fiber to avoid constipation)
- Brown rice
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Vegetables
- Dairy (to provide necessary calcium)
- Cheese
- Coconut milk
- Cashew milk
- Yogurt
- Almond milk
- Other antioxidants
- Fenugreek leaves
- Capsicum
- Tomatoes
Managing a hypothyroidism diet can be challenging during pregnancy.
Let Dr. Sergi help you create a holistic nutrition plan suited to your particular needs. She’ll include foods and supplementation aimed at treating hypothyroidism during pregnancy to support both you and your baby.
Who Should Be Treated for Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy?
If you’ve been diagnosed with hypothyroidism before becoming pregnant, you should absolutely be treated for it during your pregnancy. Thyroid hormones can fluctuate drastically throughout pregnancy, and since your baby completely relies on you for thyroid hormones in the first trimester, getting treatment right away is a must.
Women who aren’t diagnosed with hypothyroidism before pregnancy should be screened and possibly treated if they:
- Experience hypothyroidism symptoms.
- Have other endocrine system conditions.
- Have a TSH level greater than 10 mIU/L during the first trimester.
Pregnant women with TSH levels between 2.5 and 4.0 mIU/L may or may not be treated, depending on the recommendation of their doctor.
Pregnancy may increase the risk of hypothyroidism in women, especially those over 30 years old. You may also have a greater risk of hypothyroidism during pregnancy if you have:
- Goiter
- Nodules
- Had a previous thyroid condition
- Suffered from an autoimmune disorder
- Type I diabetes
HealthierU: Helping To Treat Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy Through Holistic Nutrition
At HealthierU, Dr. Donna Sergi is passionate about helping you identify and alleviate health-related symptoms by using natural remedies — and that includes hypothyroidism during pregnancy.
To ensure your body is functioning as optimally as possible during pregnancy, Dr. Sergi will design a holistic plan that includes nutritional support, supplementation, and lifestyle guidance.
Schedule a free consultation today to see how Dr. Sergi can partner with you on your journey to wellness during your pregnancy — for the benefit of both you and your unborn child.