Can Hypothyroidism Cause Inflammation in the Body? How Your Immune System May Respond to an Underlying Issue
"The content below is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition."
If an autoimmune disease is the cause of your hypothyroidism, it is a long-term condition that requires treatment. Besides the ill effects of having too little thyroid hormone, having an immune system that is constantly attacking your thyroid means chronic inflammation.
As you can imagine, inflammation that lasts longer than a normal infection or illness puts a lot of stress on the body and can affect you in many ways.
If you suspect you are experiencing chronic inflammation as a result of hypothyroidism, there is good evidence to suggest there are things you can do that may increase your well-being and health. Continue reading to find out how you can take greater control of your health naturally.
Table of Contents
Hypothyroidism and Inflammation: Are the Two Connected?
The thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3) has been found to play a key role in the maturation and function of certain immune cells (macrophages). In hypothyroidism, this role is enhanced, causing a stronger immune response.
If the proportion of T4 to T3 is too high, as is usually the case in hypothyroidism, the body’s inflammation response is more pronounced. This happens because T4 binds more readily than T3 to a specific receptor on the cell membrane. When this receptor is bound, it initiates a process that produces reactive oxygen species (ROS). These, in turn, trigger an important inflammasome (NLRP3) that activates further inflammatory responses.
This complex process illustrates in a very specific way the connection between hypothyroidism and inflammation.
What Are Some Symptoms of Inflammation That Could Be Caused By Hypothyroidism?
Chronic inflammation can affect your body in many ways. First, the symptoms that you can detect include:
- Muscle and joint pain
- Depression, anxiety, and mood disorders
- Fatigue and insomnia
- Gastrointestinal complications
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Frequent infections
Many of these symptoms are identical to those identified as symptoms of hypothyroidism, which indicates that the two conditions are closely associated.
Next, there are the more invisible effects, which include your growing risks for the following conditions:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Diabetes
- Allergies
- Arthritis and joint diseases
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Why Does Hypothyroidism Cause Inflammation in the Body?
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s disease, an incurable (but not untreatable) autoimmune condition in which the immune system cells attack the thyroid gland and cause inflammation.
Low thyroid hormone is the most urgent symptom of the condition, so it is often treated with medication that serves as an alternative source of thyroid hormone. Some symptoms such as inflammation, however, do not go away just because hormone levels are medicinally brought back to normal.
If Hashimoto’s is the cause of hypothyroidism, the body recognizes the thyroid as foreign and immune cells are sent to battle against it. The cause for this mix-up is unknown, though there are suspected culprits, including a genetic defect, a bacterium or virus, or aging. This immune system attack presents as inflammation, which is what the body needs against a true invasion by disease-causing agents.
So instead of protecting the body against disease, in this case, the immune system impairs the function of one of its most valuable organs. In a normally functioning thyroid gland, two hormones are produced: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
T4 regulates body temperature, metabolism, and mood, whereas T3 helps regulate digestive and metabolic functions. T4 is converted to T3, which is considered the more active and potent form of T4. This conversion does not just happen in the thyroid, but in other parts of the body as well:
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Muscles
- Central nervous system
- Pituitary gland
- Adipose tissue
When the thyroid is under siege by immune cells and the body is chronically inflamed, it hinders the conversion of T4 to T3 in all the areas listed above. It does this in part by reducing the expression of the enzymes that carry out the conversion and in part by causing oxidative stress, which can lead to more inflammation.
How To Treat Inflammation in Patients With Hypothyroidism
Treating hypothyroidism is necessary for the body to function normally, all the more so when you consider that
hypothyroidism and inflammation seem to form a tag team to make getting control of your health difficult. If left untreated, serious complications can occur. But take heart: many treatments are lifestyle changes that you can accomplish with the guidance of a holistic nutrition professional like Dr. Donna Sergi at
HealthierU.
6 Ways To Reduce Inflammation in the Body Caused By Hypothyroidism
#1: Take A Thyroid Medication
Your doctor can help find a medication that’s right for you — most commonly, Levothyroxine is used because it
mimics the thyroid hormone T4
(thyroxine).
Some research has indicated that levothyroxine has
anti-inflammatory effects. For instance, a
2015 study measured indicators of chronic inflammation before and during levothyroxine treatment of hypothyroidism. There was a consistent reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines and elevation of anti-inflammatory
cytokines, causing a general decrease in chronic inflammation in those patients.
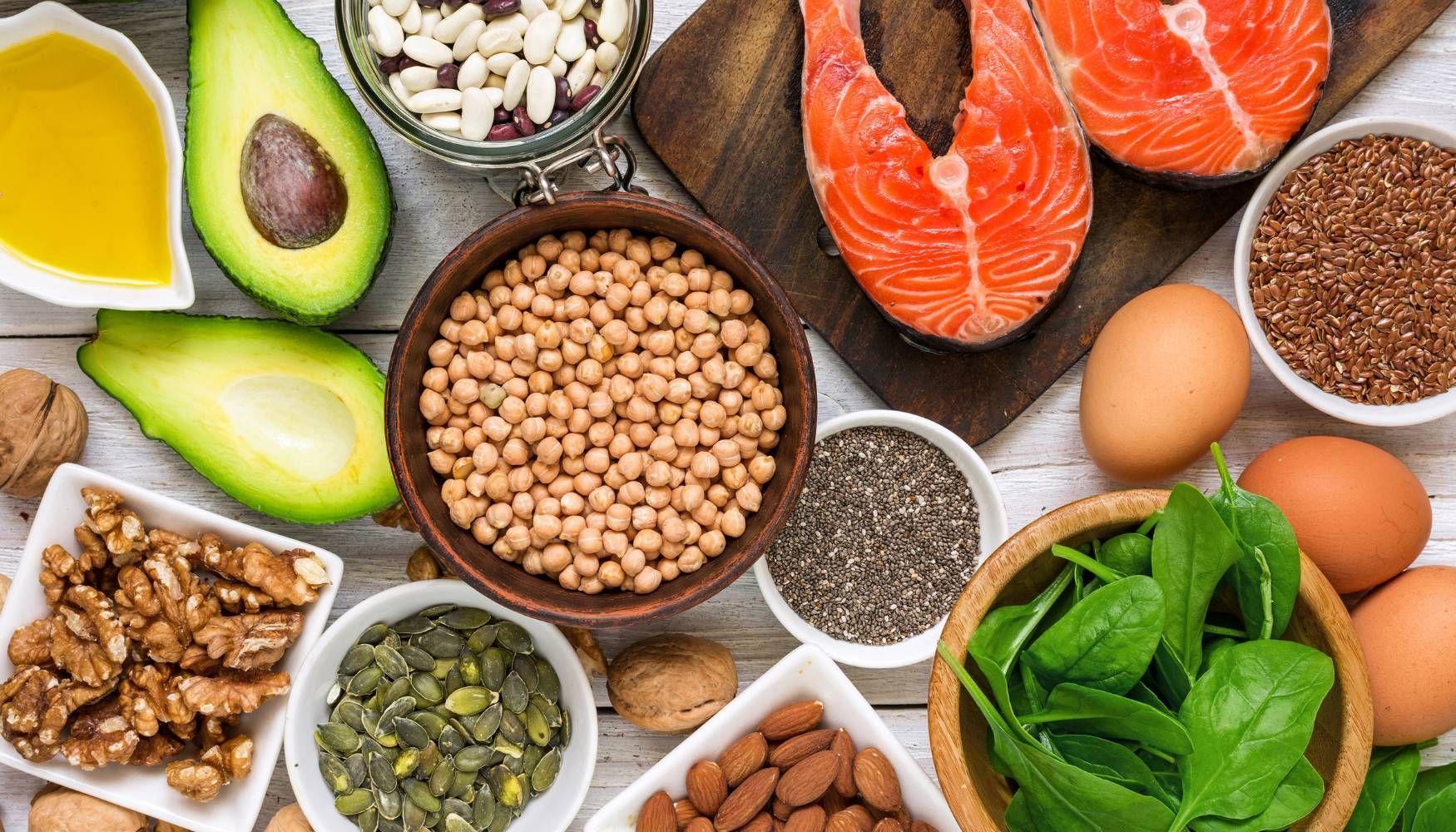
#2: Increase Vitamin and Supplement Intake
Vitamins and minerals can help address the underlying causes of hypothyroidism, chiefly autoimmunity and the inflammation associated with it. Before taking any supplement, it is important to know your current blood levels of these substances in order to avoid toxicity.
Here are some vitamins and minerals that have been found to help patients with hypothyroidism:
- Iodine: This element — found in milk, cheese, poultry, eggs, and seaweed — is essential for the production of thyroid hormone, especially in combination with tyrosine, which you can get by eating enough protein.
- Selenium: Integral to thyroid hormone synthesis and metabolism, selenium is found in the following foods:
- Seafood (salmon, tuna, scallops, shrimp, and sardines)
- Chicken, beef, and turkey
- Shiitake mushrooms
- Vitamin D: This vitamin can decrease levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is often too high in patients with hypothyroidism.
- Vitamin C: Because it is an antioxidant, vitamin C prevents damage to cells and tissues by free radicals, leading to fewer triggers for inflammation. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, bell peppers, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, leafy greens, and berries.
- Vitamin E: Found in significant amounts in sunflower seeds, almonds, and other nuts, as well as leafy greens, vitamin E is another antioxidant.
- Zinc: This element helps improve T3 levels by assisting in the conversion of T4 to T3. It is found in shellfish and mollusks, meat, legumes, and nuts.
- Coenzyme Q10: This coenzyme, which has been proven to help lower inflammatory markers, can be found in oily fish like salmon and tuna, organ meats, and whole grains.
- Omega 3s: These anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating fatty acids can be found in:
- Seafood sources (mackerel, herring, salmon, cod liver oil, anchovies, sardines, oysters, and caviar)
- Flaxseed
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Soybeans
- B vitamins: These play an important role in thyroid function and hormone regulation. Natural sources include whole grains, nuts and legumes, meat and fish, eggs, seeds, milk and yogurt, and dark leafy greens.
#3: Strengthen Gut Health
Inflammation can still be present even if you're taking medications to manage your hormones. If you’re still experiencing inflammation, it is likely due to gut health.
The gut contains 70% of the body’s immune tissue. Low thyroid hormones can compromise the lining of the GI tract, causing ulcers or allowing large protein molecules to pass through into the bloodstream. When foreign bodies enter the bloodstream an immune response is triggered, causing inflammation.
An unhealthy gut can also interfere with the activation of thyroid hormone (T3). Ways to improve gut health include:
- Eating less:
- Artificial sweeteners
- Red meat
- Processed foods
- Alcohol
- Eating more:
- Probiotics – These are the good bacteria that live in your gut. They can be found in fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha, kefir, yogurt, miso paste, and tempeh.
- Prebiotics – These are fibers that feed the good bacteria. They are present in many fruits and vegetables, including leeks, onions, raspberries, legumes and beans, asparagus, garlic, bananas, pears, and watermelons.
- Polyphenols – These are plant chemicals that good gut bacteria also thrive on. They are found in berries, apples, artichokes, red onions, tea, dark chocolate, and more
#4: Decrease Stress
Stress can increase the release of cytokines, which cause inflammation. The longer your stress persists, the greater the likelihood that prolonged inflammation will cause various conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression, and cancer.
If you are undergoing stress, you might be experiencing chronic inflammation from it. Stressors are not always easy to eliminate, but you can focus on the following things that help your body cope with them, such as:
- Getting adequate sleep
- Exercising regularly
- Having a support system of friends and family
- Making time for a hobby
- Practicing meditation and/or other relaxation techniques
#5: Eat a Nutrient-Dense, Low-Carb Diet
A diet high in carbohydrates (particularly refined carbohydrates with a high glycemic index) and omega-6 fatty acids can lead to increased inflammation.
The typical Western diet contains significant amounts of refined starches, sugars, and saturated fatty foods and too few fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which provide antioxidants and fiber.
There is evidence, however, that if you opt for a more nutrient-dense, low-carb diet, it may
reduce inflammation. This approach to food takes discipline, attention, and effort. HealthierU can assist you in making a dietary plan that you can stick to and achieve the benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet.
#6: Avoid Substances That Can Harm The Thyroid
Even if you are careful to adhere to the recommendations detailed above, It is important to keep in mind that certain foods and substances may negatively affect people with hypothyroidism. These should be avoided as much as possible:
- Cigarette smoke inhibits thyroid function and increases the risk of thyroid inflammation.
- Pesticides: Thyroid conditions are associated with exposure to environmental pesticides.
- Chlorine and fluoride can increase one’s risk of thyroid problems by displacing iodine, which is needed for thyroid hormone production.
- Millet: Although millet is an anti-inflammatory food, people with thyroid issues should avoid it because it may decrease thyroid function.
- Calcium supplements and soy can interfere with the body’s absorption of the medication prescribed for hypothyroidism.
- Uncooked
goitrogenic
foods like cruciferous veggies may also contribute to thyroid dysfunction.
Learn How To Decrease Inflammation in the Body Caused by Hypothyroidism With HealthierU
We hope you are encouraged to find that although hypothyroidism is generally a life-long condition, you do have the power to improve your health. With help from a holistic nutrition professional at HealthierU, you can soon be on the path to safely and confidently decreasing inflammation in your body.
We offer free consultations to get you started. HealthierU looks forward to assisting you as you seek to give your body the gift of more wholesome nutrition and a healthy balance of exercise and stress-relieving activities. Contact us today for our professional and personal assistance.